The ratio excludes Inventory and Prepaid Expenses because selling goods and collecting the cash takes time and is subject to market demand. The order of liquidity makes this precise order of liquidity exclusion possible, allowing analysts to gauge a company’s ability to pay off debts without relying on product sales. A higher Quick Ratio indicates a stronger, more immediate ability to service short-term debt obligations.

Why Margex Wins for Short Selling
This environment supports higher turnover and consistent quoting, which suits large, fiat-denominated execution flows. We aggregate Tier-1 liquidity across 10 asset classes, integrated directly with advanced back-office and execution technology. Managing provider performance https://content-qa.fortuneconferences.com/a-guide-to-financial-record-keeping-for-landlords/ involves regular auditing of fill times and rejection rates. You also need to verify that connection costs align with the actual effective depth delivered. Plan for new asset listings and test capacity beforehand to ensure the existing infrastructure handles the increased data load without slowing down trade processing. Managing these differences requires normalizing disparate data streams into a single standard.
What Are Deep Liquidity Pools?
A company’s order of liquidity is an important factor to consider when assessing its financial health. Accounts payable is a less liquid asset, as it represents money owed by the business to its suppliers, which may take time to pay off. This order of liquidity helps companies and investors understand the financial situation of a company and their ability to settle their liabilities. Inventories are the goods produced by a company to sell to their customers and are the least liquid current asset. The primary purpose of this ordering is to provide transparency regarding a company’s immediate purchasing power and solvency. This structure allows analysts to quickly determine how much of a firm’s value is tied up in assets readily available to cover short-term debts.

Integrate Liquidity via APIs and Trading Platforms
Financial institutions also rely on liquidity to meet their short-term obligations and manage liquidity risk. Adequate liquidity ensures that institutions can honor deposit withdrawals, fulfill payment obligations, and navigate fluctuations in funding conditions. Central banks and regulatory authorities closely monitor liquidity conditions to safeguard the stability of the financial system and prevent disruptions that could have systemic implications. Welcome to the fascinating world of finance, where liquidity plays a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of investments and financial markets. Understanding the concept of liquidity and its order is crucial for investors, financial analysts, and anyone interested in comprehending the intricacies of the financial landscape.
The Importance of Emergency Funds and How to Build Yours

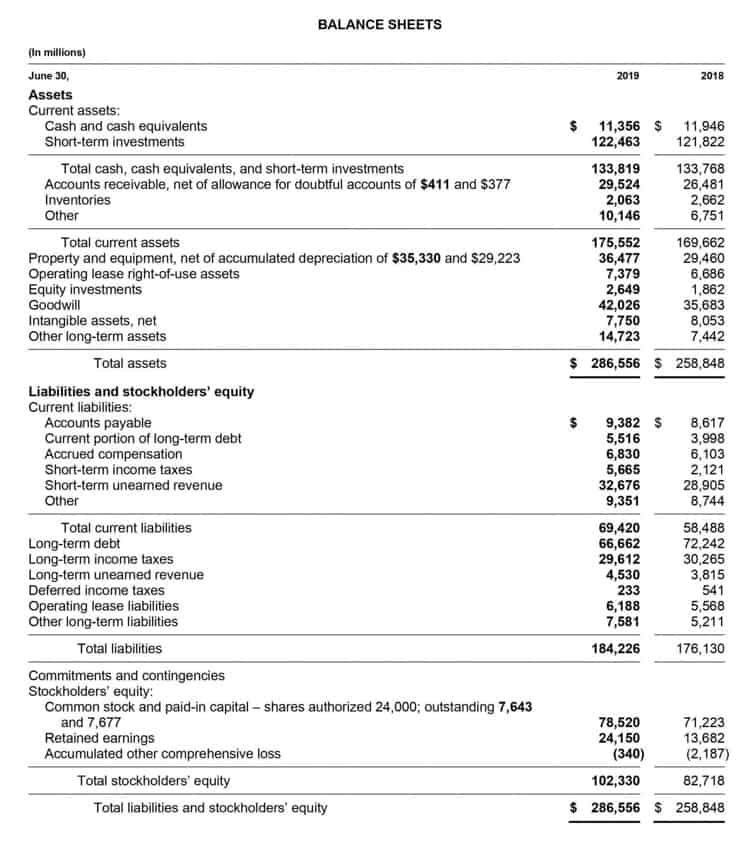
In this example, you can see that the assets and liabilities are listed in the order of their liquidity. The most liquid assets (cash) are listed first, and the least liquid (intangible assets) are listed last. Similarly, for liabilities, those that are due soonest (accounts payable) are https://www.bookstime.com/ listed first, and those that are due in the longer term (deferred revenue) are listed last.
- See the Kafka streaming documentation and sample data format for implementation details.
- For instance, if you trade a currency pair with high liquidity, your orders will be executed quickly at the expected price.
- However, sustainable success requires robust architecture and strict risk discipline rather than simple connectivity.
- The order of liquidity can also help creditors assess a company’s creditworthiness.
- This standard arrangement allows external parties like creditors and investors to easily measure a company’s liquidity.

Liquidity provider choice should map to how clients trade (size distribution, time-of-day concentration, volatility sensitivity), not to theoretical market activity. Otherwise, you risk paying for capacity your audience never uses while still failing the segments that matter most. High-frequency scalpers demand tight spreads to capture small movements efficiently. Conversely, institutional clients prioritize substantial market depth to fill large block orders without causing significant price impact. Aggregation technology addresses market fragmentation by unifying distinct liquidity streams. Prime-of-Prime (PoP) brokers connect Tier-1 banks, non-bank market makers, and exchanges to create a deep “virtual” order book.